SEVIRI
LST (Land Surface Temperature; Atitar and Sobrino, 2009)
LST is estimated for day- and night-time acquisitions using the method developed by Atitar and Sobrino (2009):
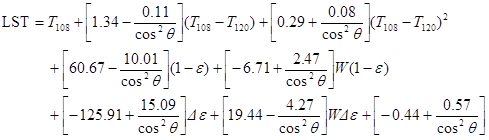
SST (Sea Surface Temperature; Romaguera et al., 2006)
SST is estimated for day- and night-time acquisitions using the method developed by Romaguera et al. (2006):
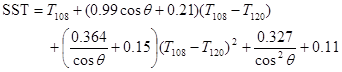
References
Atitar, M. & Sobrino, J. A. (2009). A split-window algorithm for estimating LST from Meteosat 9 data: test and comparison with in situ data and MODIS LST, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol. 6, No. 1, 122-126.
Romaguera, M., Sobrino, J. A. & Olesen, F.-S. (2006). Estimation of sea surface temperature from SEVIRI data: algorithm testing and comparison with AVHRR products, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 27, 5081-086, 2006.